Applying Python Scripts in Rulex Processes
The Python Bridge task allows you to perform statistical calculations via Python script on Rulex data, and either overwrite the original dataset with the output results, or create a new dataset (such as clusters or advanced association structures).
This type of task may be useful when you already have statistical algorithms in Python, and want to use them in Rulex without having to rewrite any of the logic.
The Python script can either be entered directly in the task, or a reference can be provided to an external script file.
Python dictionary format
The format data in python is a dictionary that associates to each column name (key) the list of values of the column itself (values), for example:
"age" : [39, 45,...]
"workclass" : ["Private", "State-gov",...]
Prerequisites
Python 3 software has been installed where Rulex is running.
IPython3 has been installed on the machine where Rulex is running (via pip install ipython)
Additional tabs
The following additional tabs are provided:
Documentation tab where you can document your task,
Parametric options tab where you can configure process variables instead of fixed values. Parametric equivalents are expressed in italics in this page (PO).
Procedure
Drag and drop the Python Bridge task onto the stage.
Connect the task that contains the dataset on which you want to perform the Python script to the Python Bridge task.
Double click the Python Bridge task.
Configure the script options as described in the table below.
Save and compute the task.
Python bridge options | ||
|---|---|---|
Name | PO | Description |
General options | ||
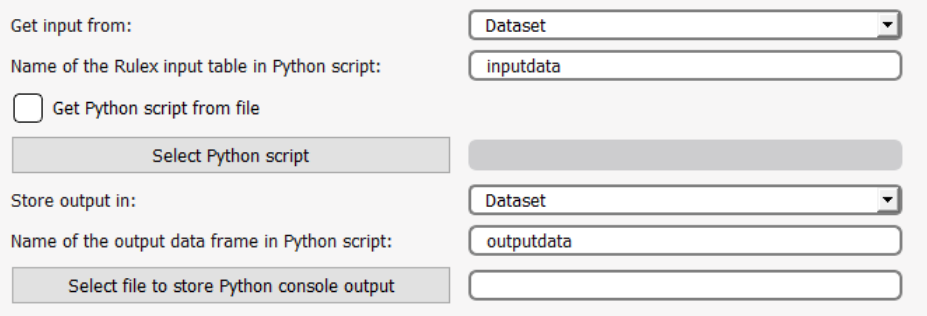
Get input from | setref | Select the type of data you want to use as input for the Python script. Possible options are:
|
Name of the Rulex input table in Python script | rinputname | Enter the name you want to use within the Python script to reference the data received from Rulex. For example, if you selected Dataset in the Get input from option, and you enter Input as the name here in this option, the main Rulex data table will be referred to as a dictionary called "Input" within the Python script. |
Get Python script from file | scriptfromfile | Select this option if you want to reference an external script file. Alternatively you can enter the script code directly in the Python Code edit box below. This edit box will be disabled if you decide to reference an external file to avoid confusion on which script will be applied. |
Select Python script | filename | Click here and browse to the external file, which contains the Python script you want to apply. This option will be enabled only if you have selected the Get Python script from file option. |
Store output in | outref | Select the type of table that will be populated by the dictionary selected as output in the Python script. Possible options are:
|
Name of the output dictionary in Python script | routputname | Enter the name you want to use in the Python script to reference the data Rulex will receive from Python. This data will populate the table according to the option selected in Store output in. |
Select file to store Python console output | debugfilename | Browse to the text file where the Python script console output will be saved after execution of the Python Bridge task. |
Python Code | rcode | Enter the Python script code you want to execute. This text box is enabled only if you ave not selected the Get Python script from file option. |
Connection options | ||
Select path to Python command | rcommand | Browse to the location of the IPython interpreter command, which can be found in the Python installation folder. If you have administrator rights on the machine, it will be sufficient to enter ipython3.exe. If the path is not correctly specified, the Python Bridge task will not work correctly and a warning message will be displayed. The Python task cannot compute if another process is pending. You can monitor this on Windows via the Task Manager (Processes). |
Python host | rhostname | Enter the address of the host where Python is installed. If Rulex is running on the same desktop where it is installed you can enter localhost. |
Python port | rport | Specify the port used for data transfer between Rulex and Python (i.e. input table transfer from Rulex to Python, output dictionary transfer from Python to Rulex). System firewall exception Make sure you define an exception in the system firewall on this port, allowing the data exchange between the two applications. Otherwise, the task will not be executed and a warning message will be displayed signaling a communication problem between Rulex and Python. |
Python port for signals | rportaux | Specify the port used for signal transfer between Rulex and Python (i.e. progress bar updates). System firewall exception Make sure you define an exception in the system firewall on this port, allowing the data exchange between the two applications. Otherwise, the task will not be executed and a warning message will be displayed signaling a communication problem between Rulex and Python. |
setprogress command
The setprogress command, which updates a progress bar, increasing it by a corresponding progress percentage, can be set via the Python code text box, or via a referenced external script.
For instance, if the current progress value is 10 and a setprogress(10) command is executed, the progress bar is increased by (100-10)*10% = 9%, that is to 19%.
If Python libraries are referenced in the script (through the “library” Python instruction), you should install them previously, in their native Python environment, instead of inserting the install.packages instruction directly in the Python Code window. However, the install.packages command can be run from Rulex only if Rulex itself is executed with administrative privileges: otherwise, a warning concerning this issue will be raised and the execution will not terminate.
Example
The following example is are based on the adult dataset.
In the scenario a very basic Python script will be applied to Rulex data, and the results will be viewed in a Data Manager task.
Scenario data can be found in the Datasets folder in your Rulex installation.
The following steps were performed:
We then add a Python Bridge task and enter the Python script code directly in the task options.
We finally use the Take a look function to check the results of the R script.
Procedure | Screenshot |
|---|---|
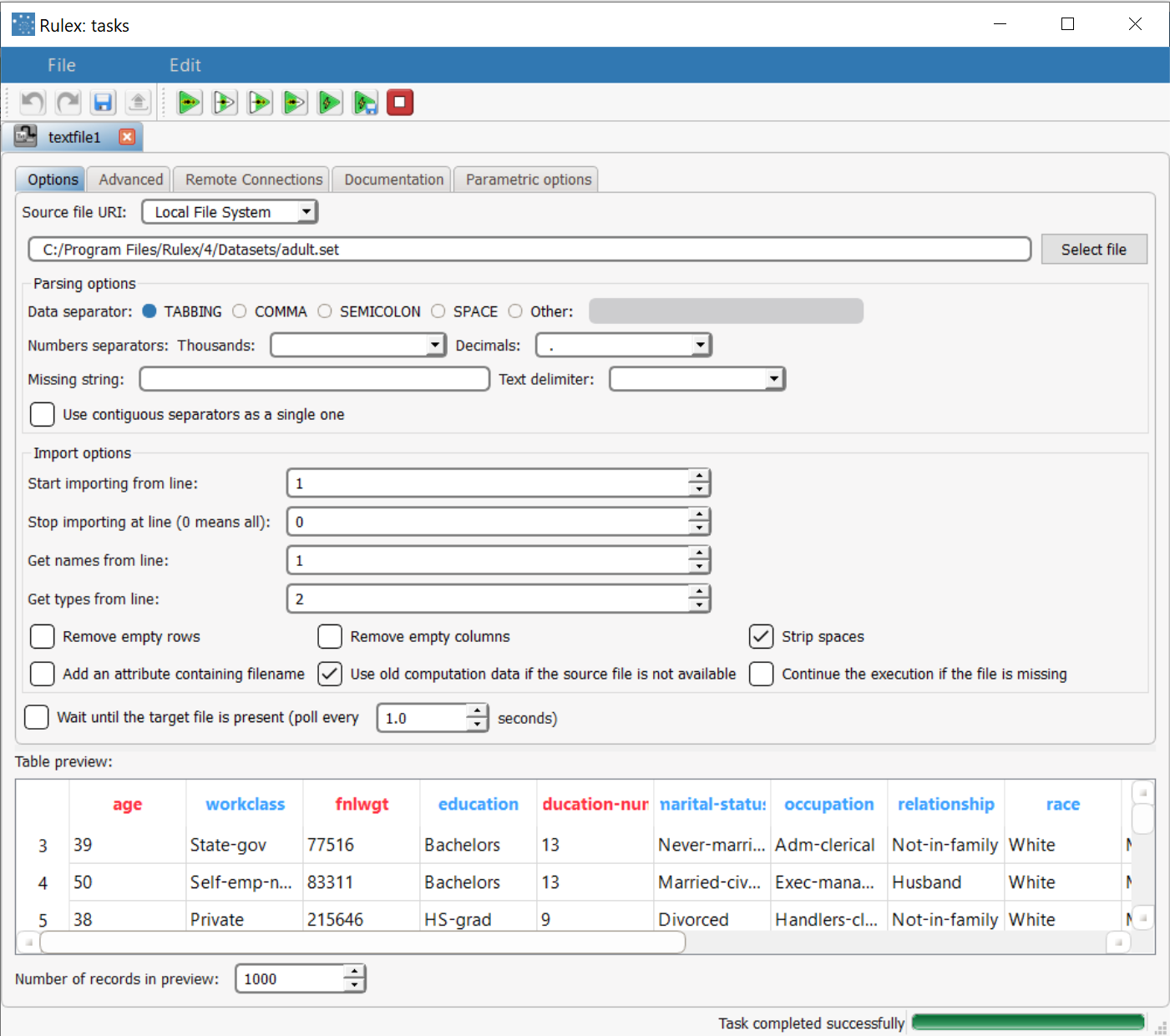
Importing the adult.set dataset via an Import from Text File task, taking the data types from line 2. | |
Add a Python bridge task to the process and configure it as follows:
| |
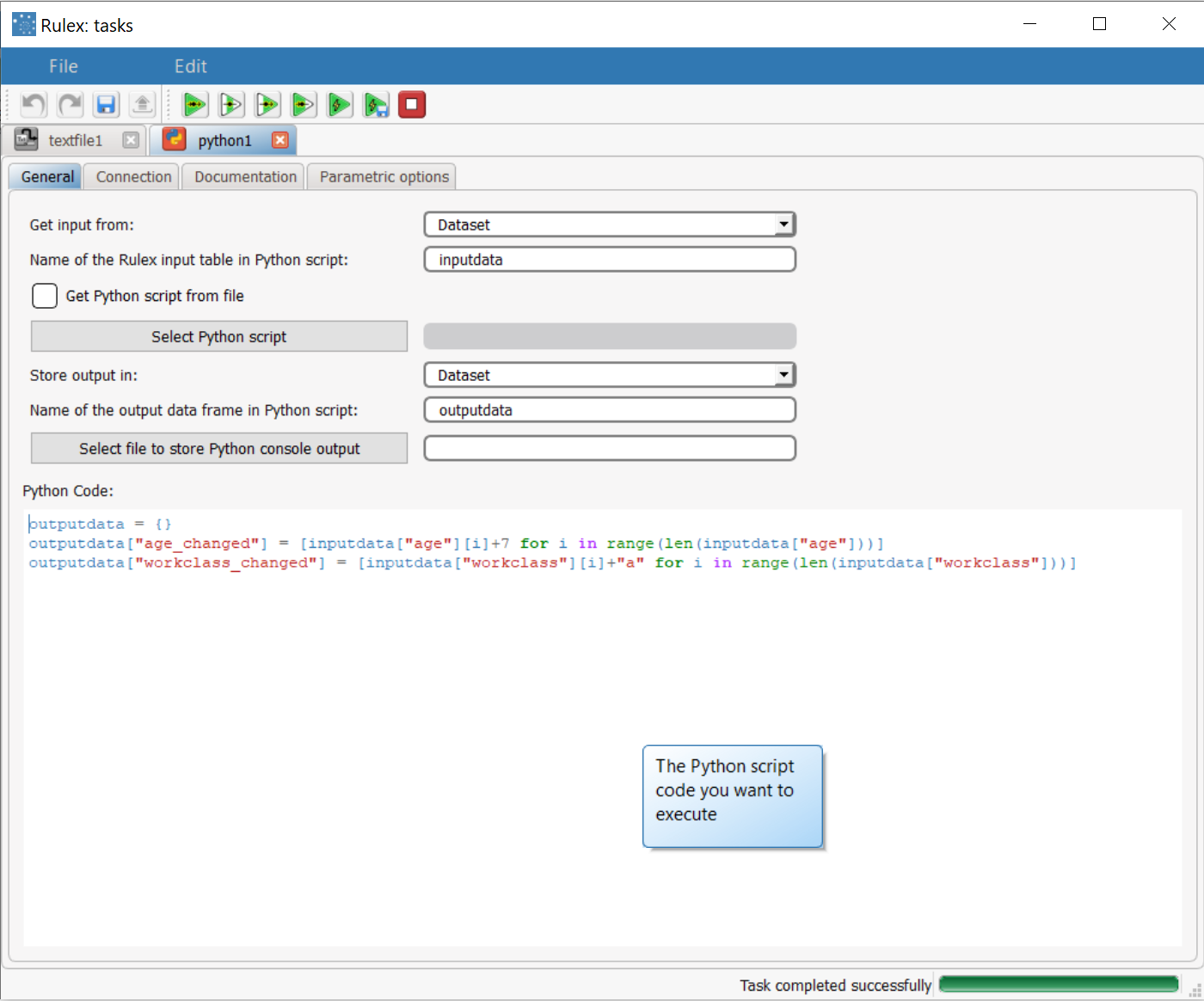
Enter the following script in the Python Code text box: outputdata = {}
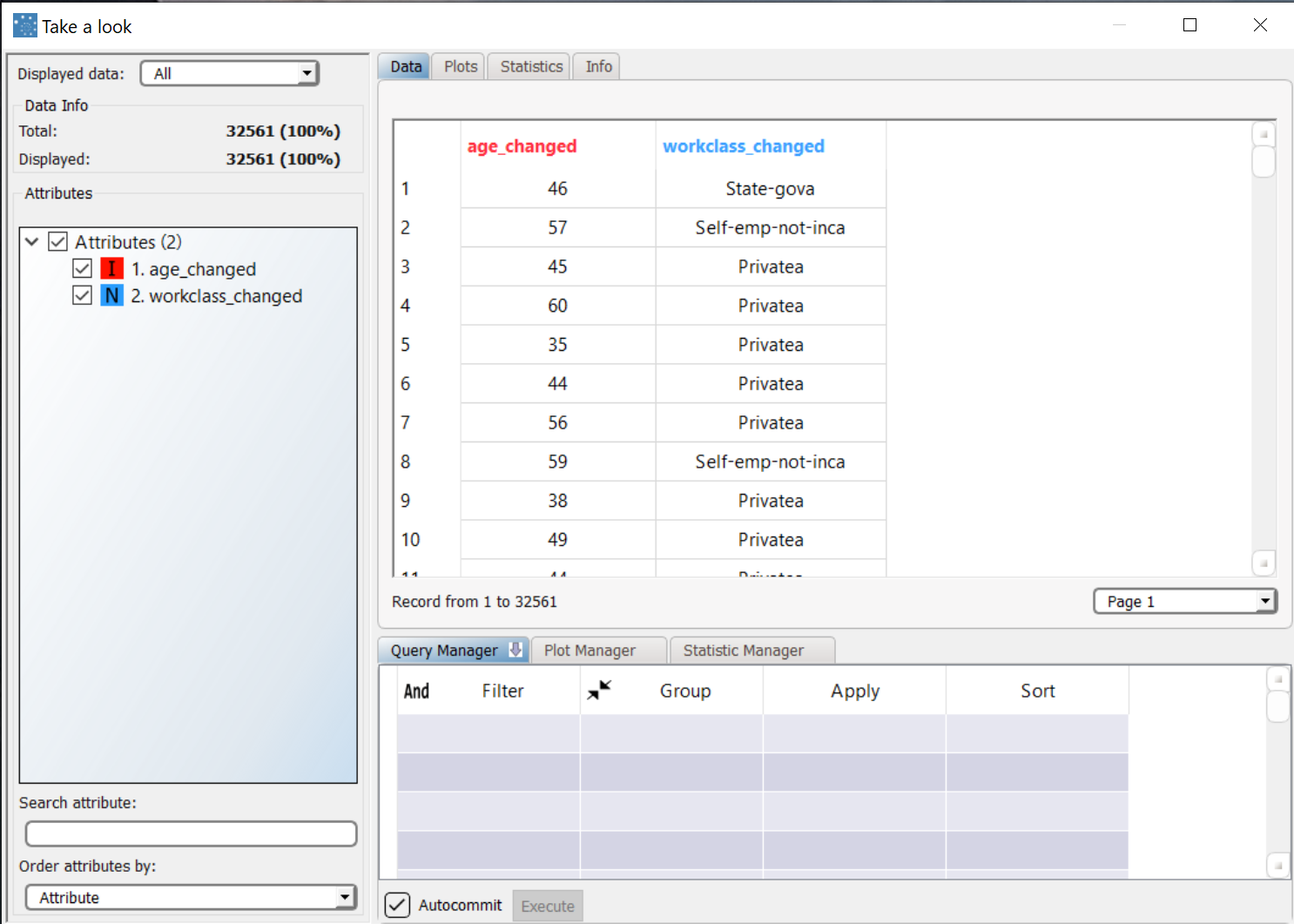
outputdata["age_changed"] = [inputdata["age"][i]+7 for i in range(len(inputdata["age"]))]
outputdata["workclass_changed"] = [inputdata["workclass"][i]+"a" for i in range(len(inputdata["workclass"]))]
The code simply creates:
| As specified by the values set for the options Store output in and Name of the output data frame in Python script, the Python Bridge task will overwrite our dataset with the content of the dictionary named output in our script (if no dictionary named output were found, a warning message would be raised). Then, as we can see in the final lines of the script, we create a dictionary named output and we populate it with the result of the two tests. |
In the Connection tab, configure the following:
| |
Save and compute the task, then right-click it and select Take a look to explore the results. The two new columns have been created by the Python script, as we expected. |