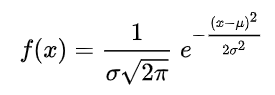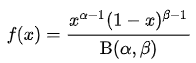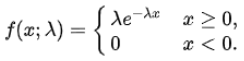Plotting Q-Q Plots
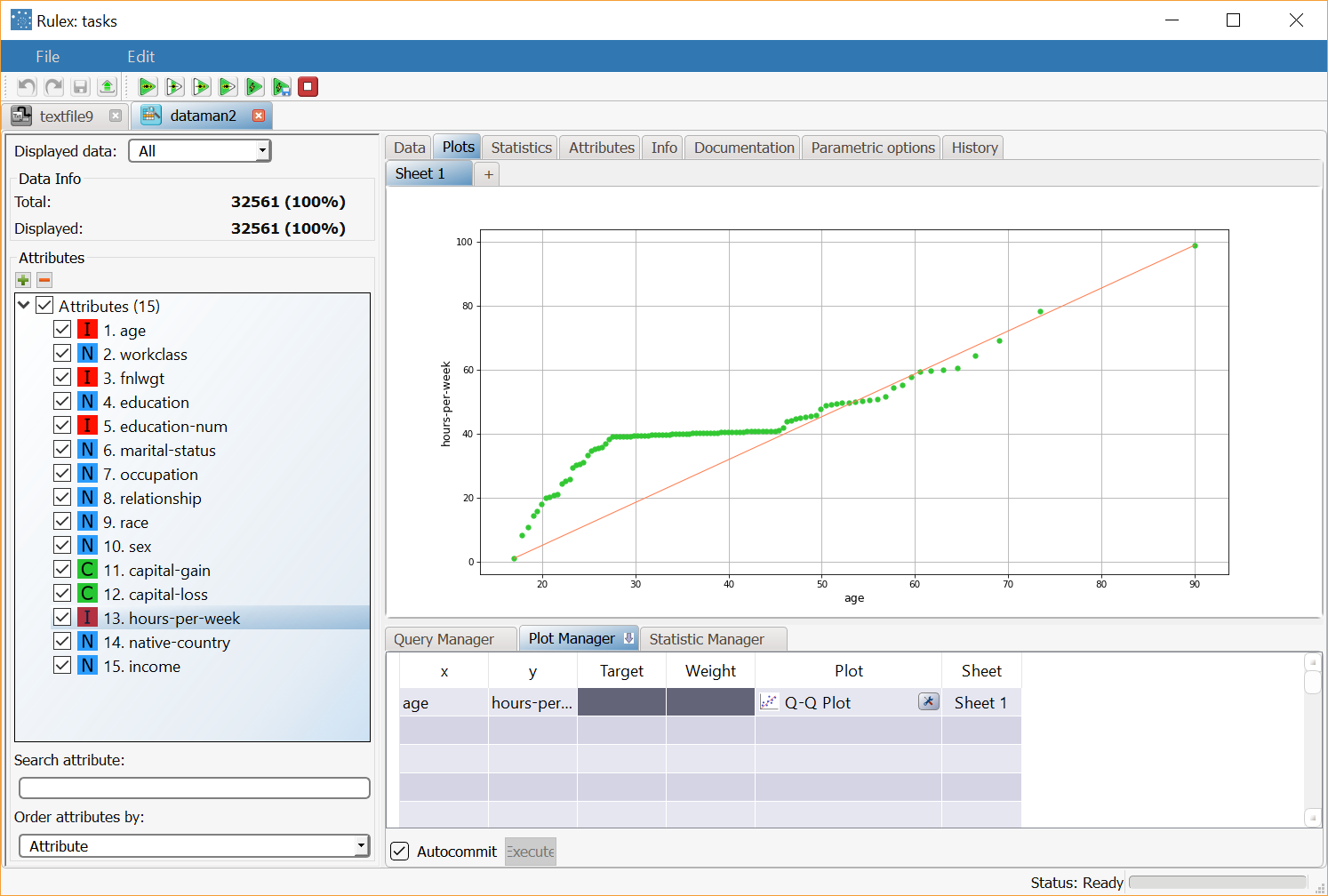
A Q-Q Plot (Quantile-Quantile Plot) is a probability plot used to compare two probability distributions by plotting their quantiles against each other. If the two distributions being compared are similar, the points in the Q-Q plot will approximately lie on the line y = x. In a Q-Q plot it is possible to compare two empirical probability distribution or an empirical one with a standard probability distribution.
It contains the following attributes:
Attribute | Mandatory | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
x | Either x or y must be specified | It cannot be a nominal value |
y | Either x or y must be specified | It cannot be a nominal value |
Properties
The following example is based on the Adult dataset.
Scenario data can be found in the Datasets folder in your Rulex installation.
Category | Properties | Description |
|---|---|---|
General parameters | Compared distribution | The distribution comparison mode can be selected from the following values, consequently selecting he corresponding options below. Possible values are normal, beta or exponential. |
General parameters | Number of quantiles | Defines the number of quantiles displayed in the plot. |
Normal distribution parameters | Mean | Normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution where values are symmetrically distributed around the average value, defined here as the Mean μ. The Standard Deviation σ defines how far the displayed values can deviate from the mean. Normal distribution is defined as follows: where:
|
Standard deviation | ||
Beta distribution parameters | Alpha | Beta distribution displays a probabilistic display of probabilities, by defining Alpha (α) and Beta (β) values, which will be used to define the distribution as follows:
where:
|
Beta | ||
Exponential distribution parameters | Lambda | Exponential distribution calculates the time which occurs between two events, where the Lambda (λ) value specified here is the average number of events in 1 unit of time. The exponential distribution is given by: |
Examples
The following examples are based on the Adult dataset.
Type | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
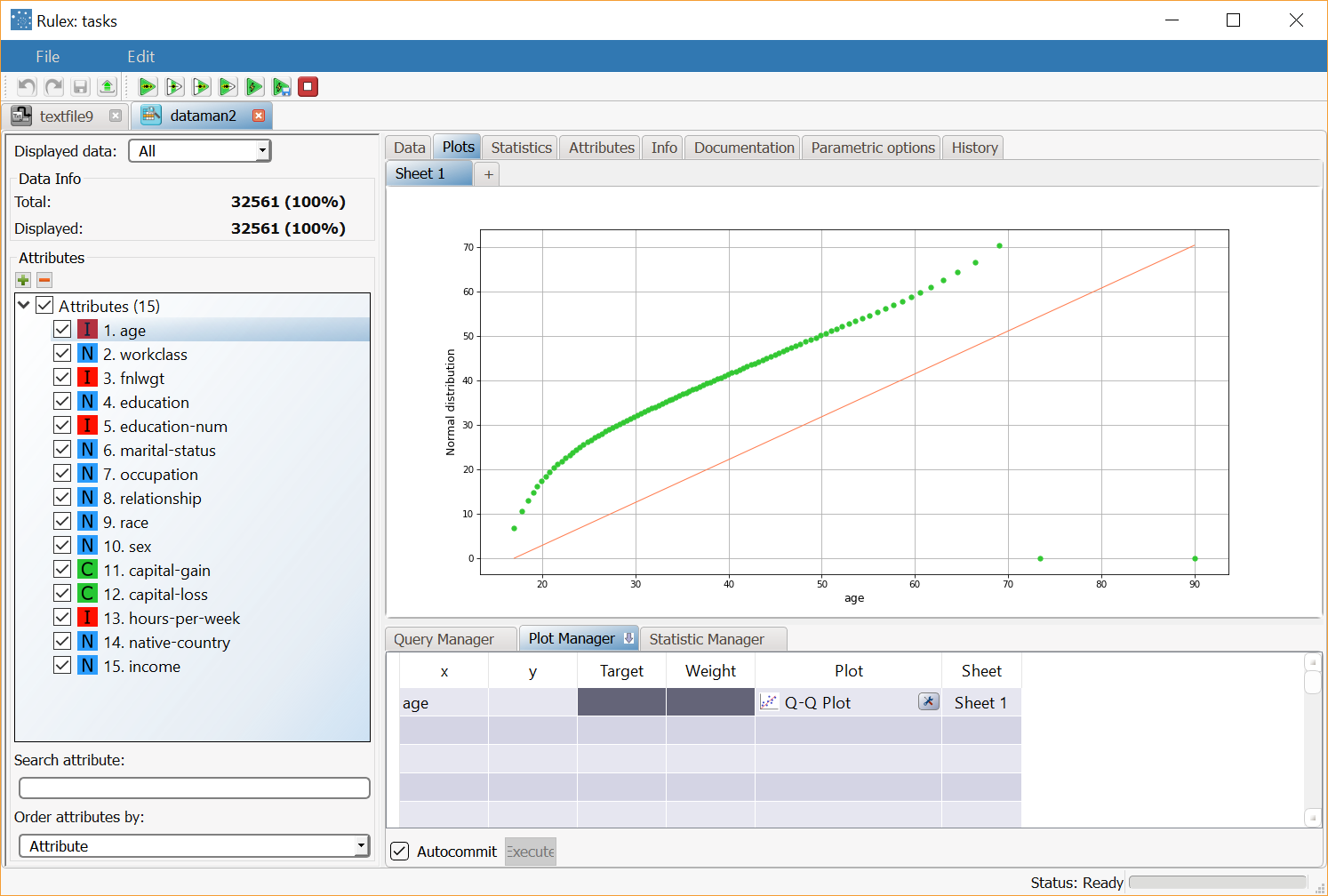
Basic Q-Q plot with x attribute only | Dragging and dropping the age attribute onto an x cell and selecting Q-Q Plot in the Plot cell will display the Q-Q plot of the age attribute compared with the Normal distribution (default comparison). | |
Basic Q-Q plot with x and y attributes | Dragging and dropping the hours-per-week onto a y cell will display the Q-Q plot of the age attribute compared with the hours-per-week distribution. |