Joining Datasets
The Join task in Rulex merges two datasets by their rows, creating a single table with all the data.
Merge operations can be used to produce a global dataset from on which in-depth analyses can be performed.
All merge operations are performed around the key attributes, which act as a unique identifier of each row in a table.
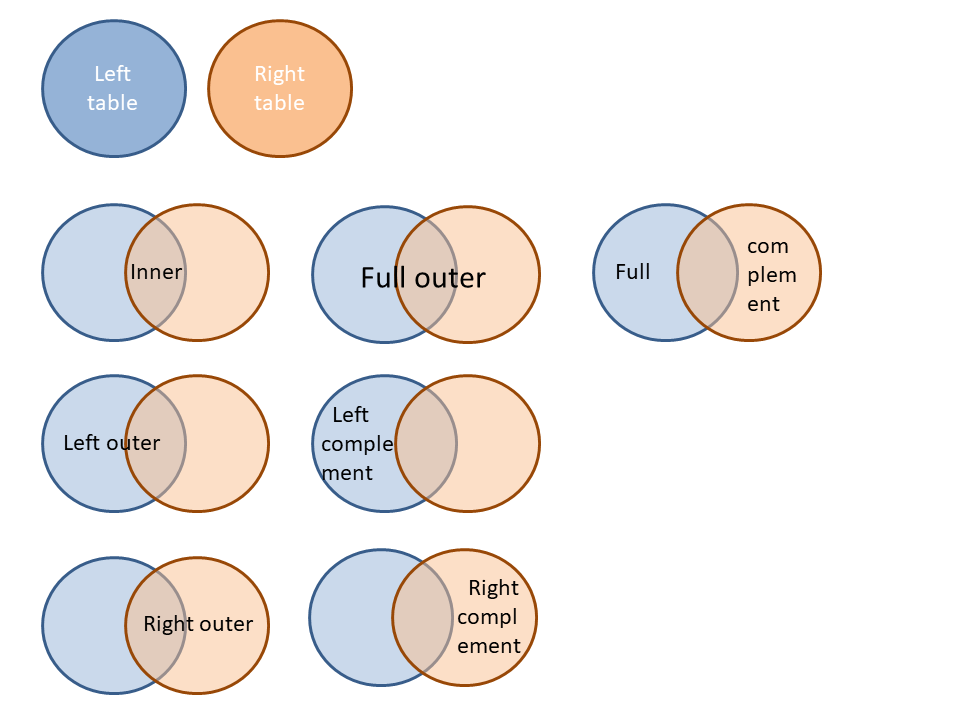
Rulex offers a full range of join options:
Prerequisites
the required datasets have been imported into the process.
Additional tabs
The following additional tabs are provided:
Documentation tab where you can document your task,
Parametric options tab where you can configure process variables instead of fixed values. Parametric equivalents are expressed in italics in this page.
Procedure
Drag and drop the Join task onto the stage.
Connect the tasks that contain the datasets you want to merge to merge the Join task.
Double-click the Join task.
Select the attributes you want to include in the merged table from the list of attributes on the left (lkeepnames) and right side tables (rkeepnames).
Configure the options described in the table below.
Save and compute the task.
Join options | ||
Name | PO | Description |
|---|---|---|
Join type | jointype | Select the combination method you want to use from the Join type drop-down menu. Possible types are:
|
Missing policy | misspolicy | Select the policy you want to adopt for managing missing values when evaluating the constraints on the matching attributes:
|
Merge type | mergetype | This option manages attributes with the same name (or the same position according to the Match columns by name options) that are present in both datasets. Possible merge types are:
|
Match columns by name | byname | If selected, columns with the same name are considered equal (default), rather than in the same position. |
Matching attributes for joining datasets | lkeynames, rkeynames, oplist, parlist | Drag and drop the key attributes you want to use to combine the datasets from the left-hand dataset (lkeynames) and right-hand dataset (rkeynames) onto the Matching attributes panel below, specifying the relationship that must exist between each pair of attributes with an operator (oplist) and value (parlist). If no attributes are selected row numbers are employed to combine datasets. A search and order function is provided to make it easier to find attributes when the list is long:
More than one attribute can be defined as key, however the number of attributes must be the same in both panels. |
Insert left key value when missing or Insert right key value when missing | leftfill, rightfill | Select Insert left key value when missing or Insert right key value when missing if you want all the key attributes that are not present in a dataset to be filled with the corresponding key value in the other dataset. |
Example
The following examples are based on the Northwind dataset.
Scenario data can be found in the Datasets folder in your Rulex installation.
The following steps were performed:
We then import the northwind_orders.set dataset.
A Join task is added to create a single dataset.
Use the Take a look functionality to check the joined datasets.
Procedure | Screenshot |
|---|---|
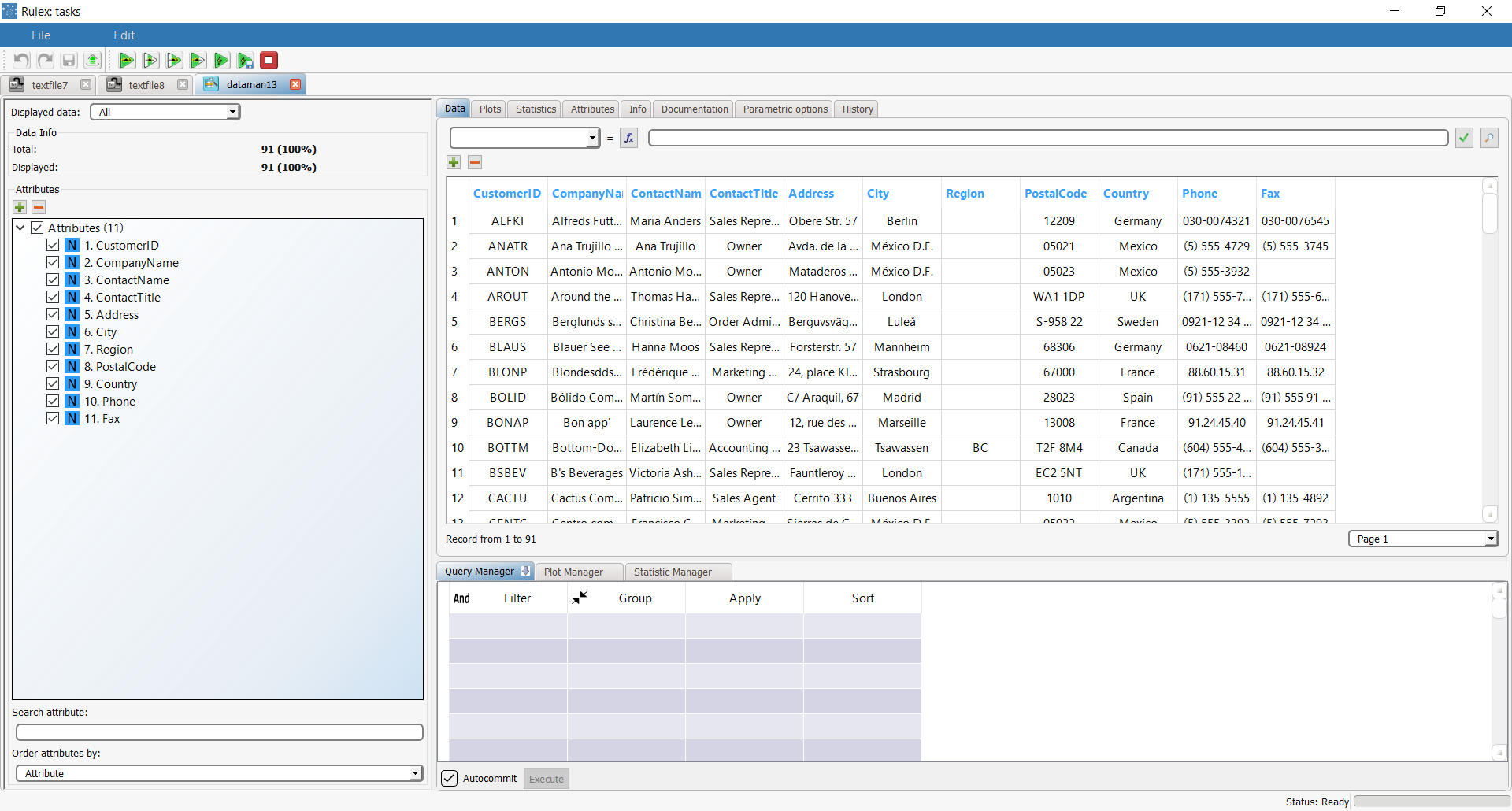
Import the first northwind_customers.set dataset, and compute the task. To check its data, right-click the task and select Take a look. The dataset is related to customers and contains:
| |
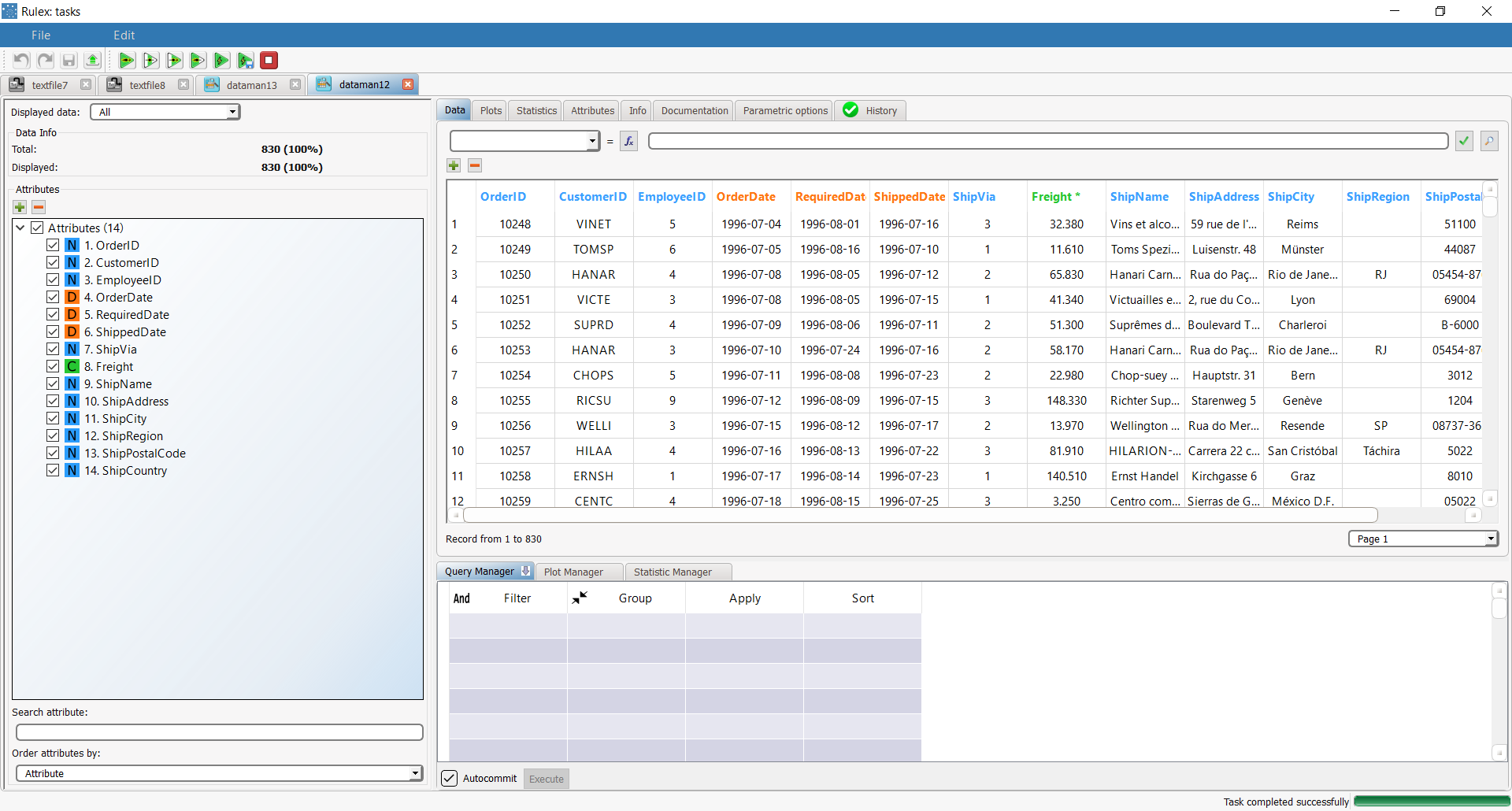
northwind_orders is related to orders and contains
| |
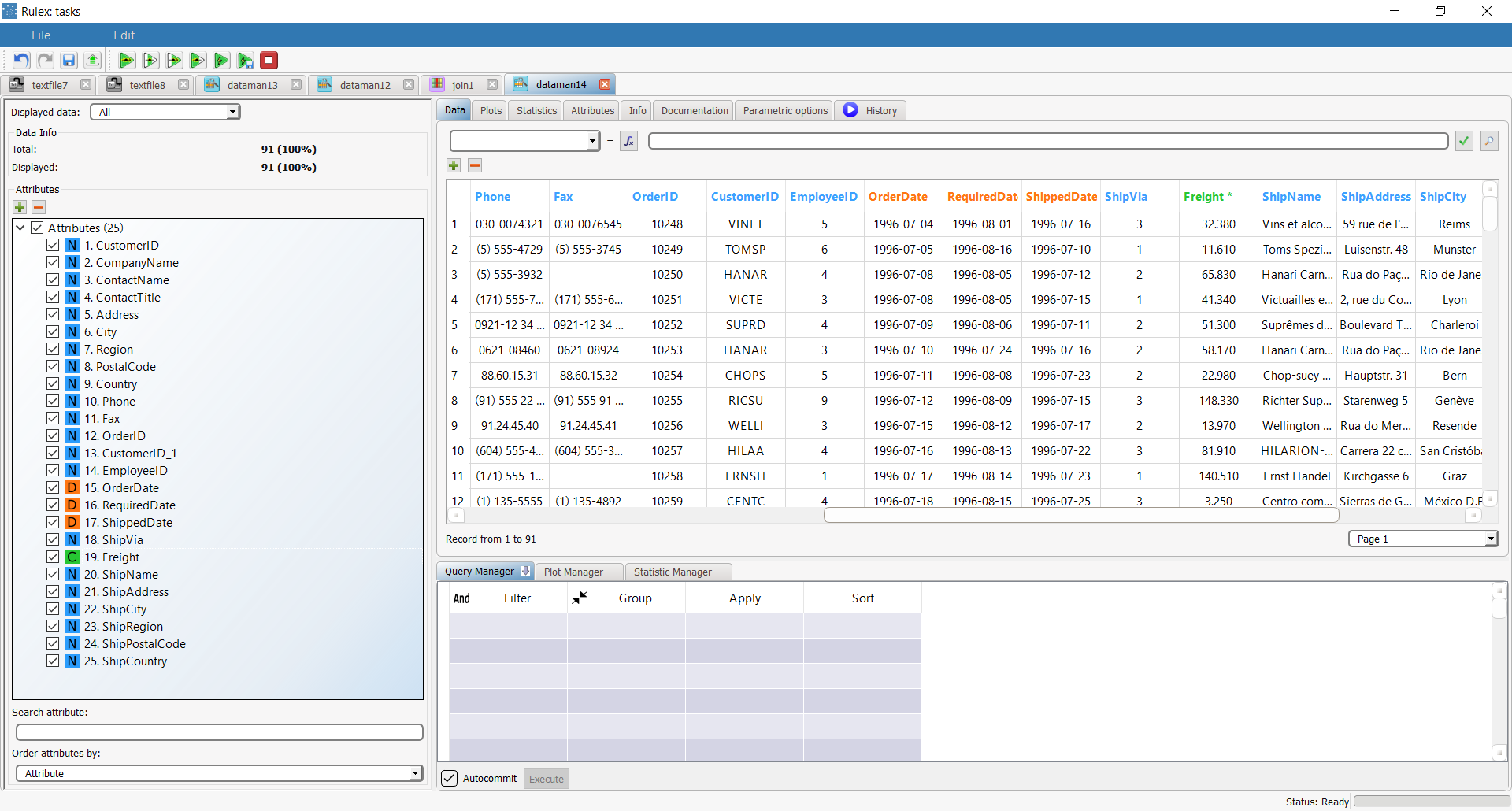
Add a Join task to the process. If the task is executed with the default options no attributes are present in the matching panels and therefore the row numbers are employed to combine datasets. In this case the resulting table has 91 records with 25 attributes. Note that the name CustomerID of the first attribute deriving from the right dataset has been changed to Customer_ID_1 to avoid a conflict with the name of the first attribute. | |
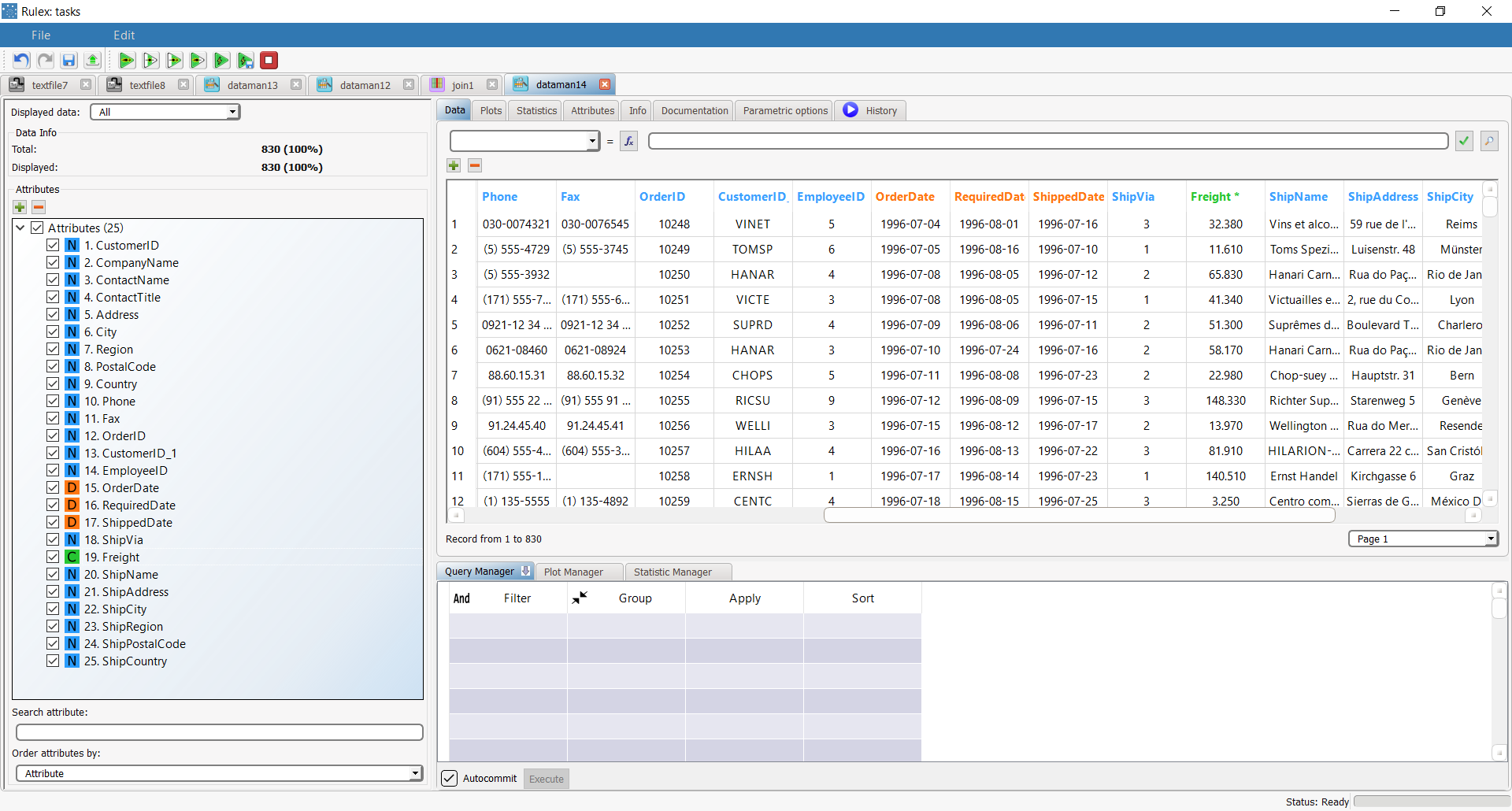
If the Right outer join is selected as the Join type, the resulting dataset has 830 rows (same as the right table) and all the attributes from the left dataset are filled with missing values from rows 92 on. | |
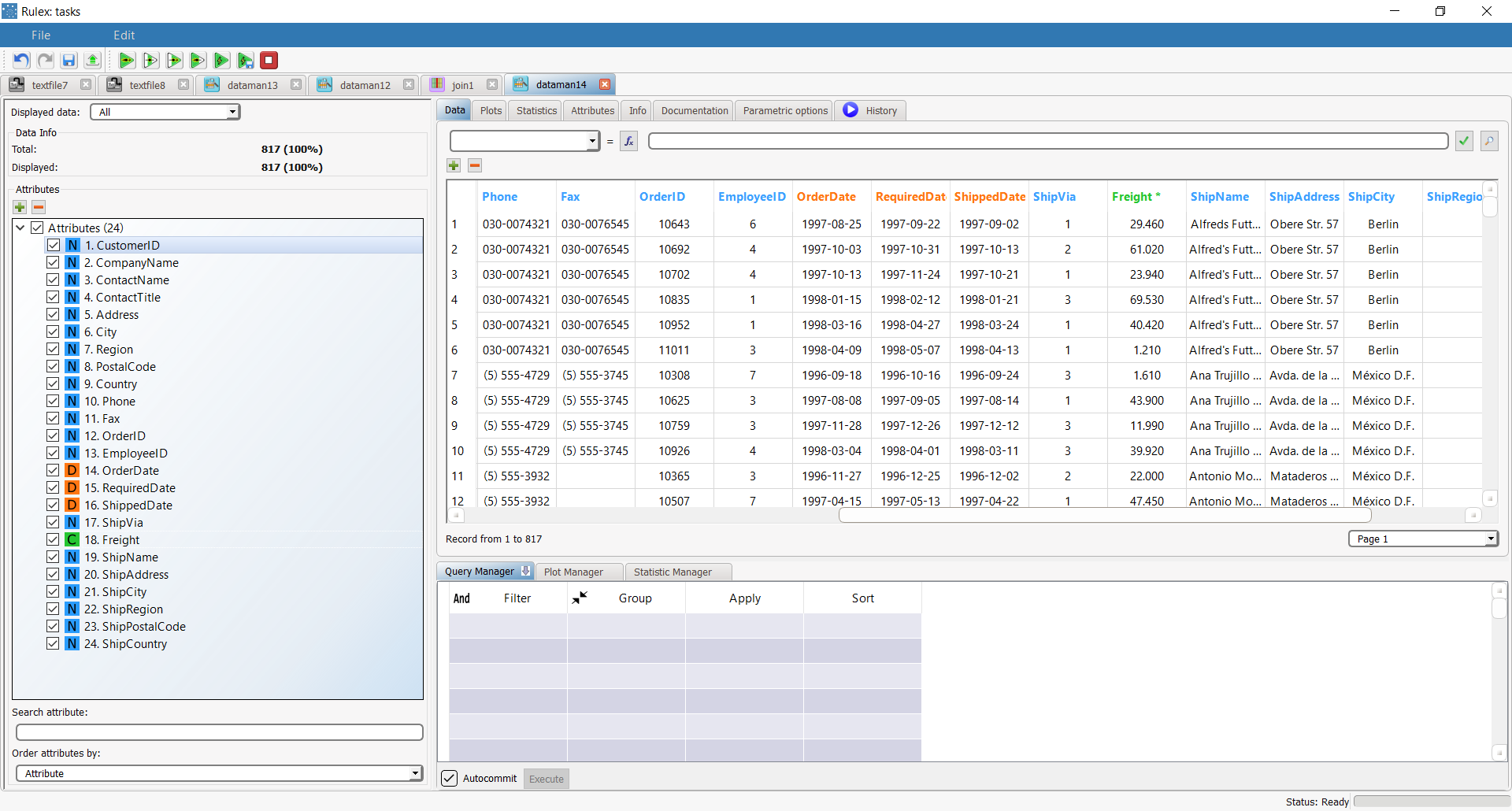
If the CustomerID and City attributes from the dataset on the left are matched with the CustomerID and ShipCity attributes from the dataset on the right, and Inner join is chosen as the Join type, the resulting dataset includes 817 records with 25 attributes. Only 817 different values in the CustomerID/ShipCity attribute pair from the right dataset match the values in the CustomerID and City attribute pair from the left dataset. | |
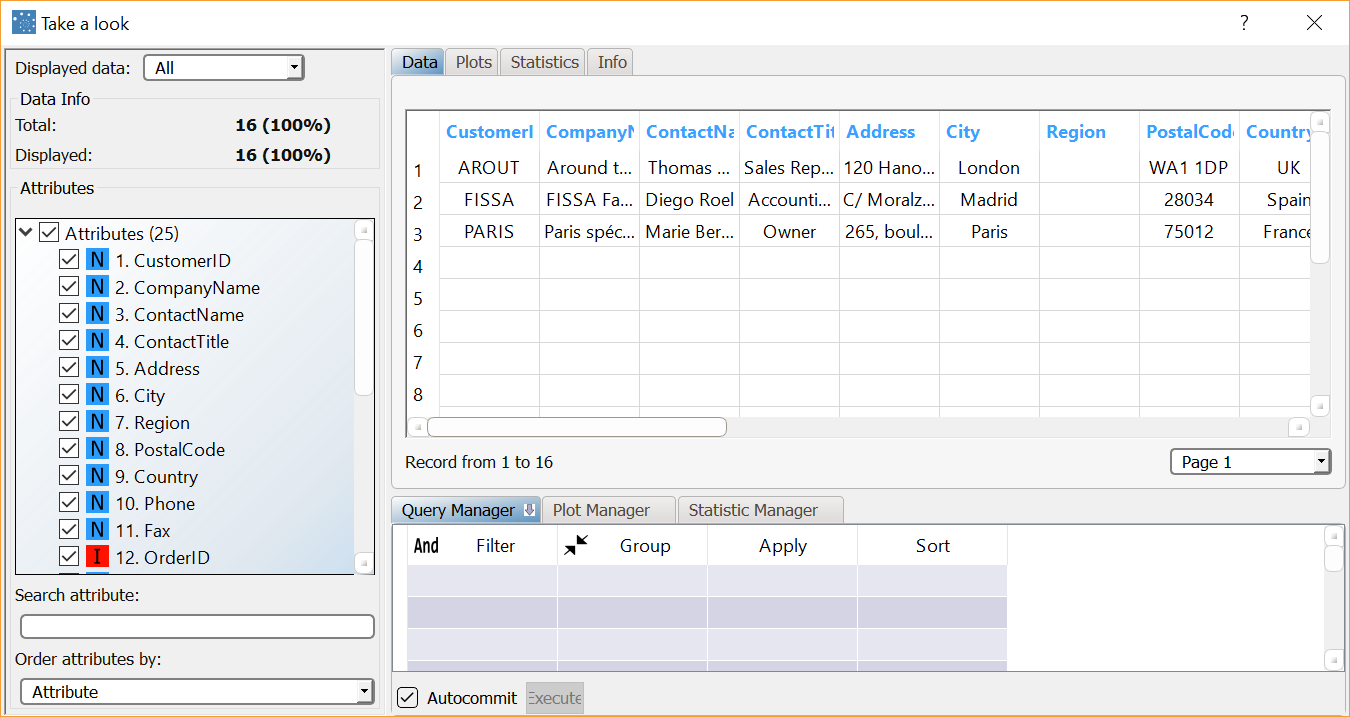
If the Full complement is selected as the Join type for task join1, the resulting dataset includes 16 records. |